Adapting Education For Future Skills Through Deep Learning Through Active Participation: Reimagining the Classroom
December 15, 2025
Big changes are happening in academics. The reason: new educational concepts are emerging--adapting education for future skills. This will shape classroom teaching and decide how learning happens for all students. Importantly, what happens with it is that educators shift their role. They stop just delivering content and facilitating environments.
With this, learners engage, experiment, reflect, and build real competence. At the centre: deep learning through active participation is needed in education.
However, with tools like AI-based eLearning, data-driven improvement can be utilized for improving the curriculum content.
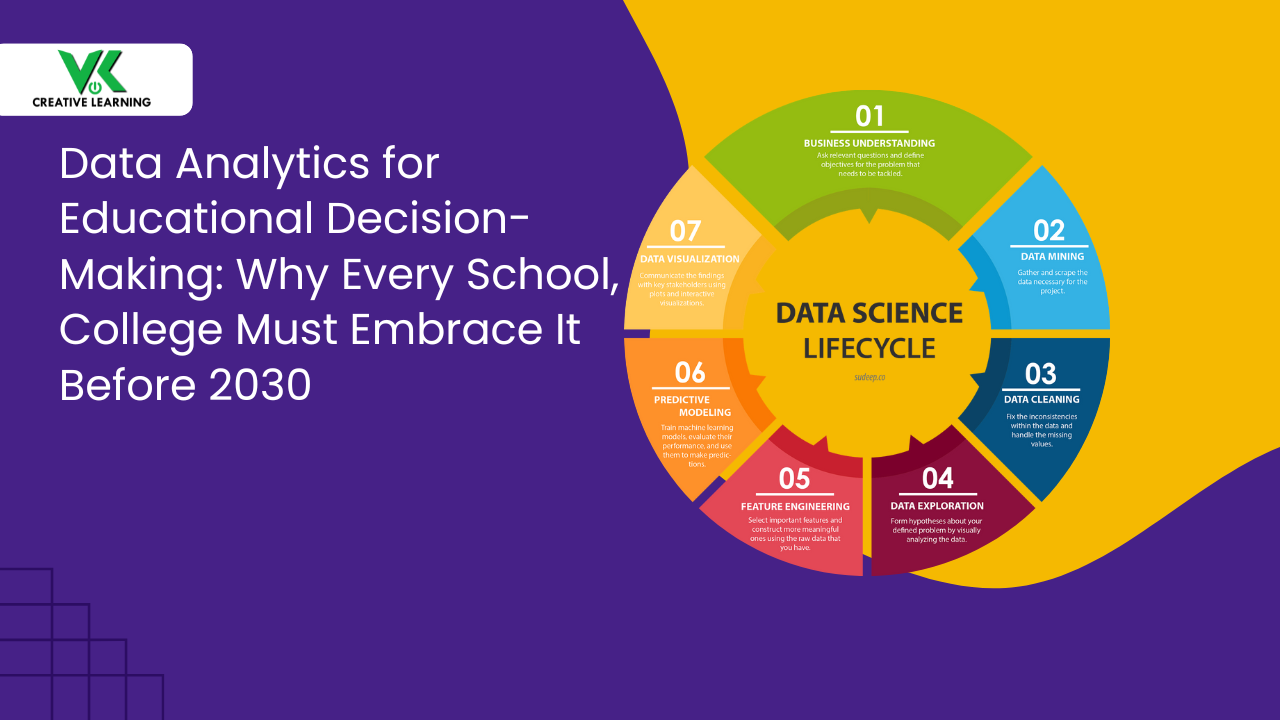
Besides, the incorporation of analytics in the eLearning platform helps track progress
With platforms like K-12 eLearning or undergraduate courses, data can be collected. Importantly, what happens with it is that analytics help students' learning growth. This spot is exactly where students need extra help; best: it ensures quality education for all.
Platforms like academic graduate eLearning also keep colleges aligned with job markets; also, classrooms evolve to keep up.
This way, learners get more than just memorized facts; they acquire skills that last a lifetime. That is, students go beyond rote learning--learners probe and apply learned knowledge.
The best epitome would be: eLearning offers adaptability. This aids students in knowing how to solve tough problems. Besides, eLearning helps to figure out how students think as data is present. Simply put, these skills hold real value--that too in any job.
Understanding Future Skills and Their Relevance
Primary Skill Horizon and the Workplace Shift
The world is morphing at a brisk pace; the cause: future skills matter. This includes evolving tech, and new concepts are introduced. So, moving in sync with circumstantial change is essential for students.
In simple words, what happens with it is that education must adapt--that too as per what the time demands. This is highly necessary as this will shape how teaching happens for all students. Learners need flexible competency, not just domain knowledge.
The best exemplar would be: the financial sector. Through corporate eLearning training, junior analysts can get an idea about how global markets are changing.
Deep Learning By Active Participation
Deep learning of students and programming deep neural networks are closely related. Elaborating on this, deep learning refers to learners’ concepts being made stronger and related to real-life practice.
In fact, this can happen through active participation (through eLearning simulation, interactive animations) improves learning.
To add to this, the use of deep learning methods in eLearning enhances and develops knowledge expansion. Besides, the use of deep learning through active participation develops critical thinking and increases retention.
In the reimagined classroom, students get their hands dirty rather than tuning out. They do, reflect, and iterate through action--practice for understanding complex principles. This is the heart of transforming capacity into actual ability--adapting education for future skills.
Data-Driven Educational Improvement
To sustain a change in the educational quarter, institutions need to intentionally utilize data. That is, by tracking their learning engagement patterns, growth paths, and feedback loops. Colleges and institutions then need to adapt the content and provide the necessary support.
For example, tracking of their learning data may indicate that certain learners struggle with abstract explanation. This means ongoing micro-intervention supports can be developed. Later, this can be provided quickly through an eLearning platform.
This ensures inclusive quality education where no one is left behind. Especially, because the pedagogical model is a one-size-only teaching methodology.
Implementation Across Domains with Real-Life Examples
In the Educational Sector: Schools and Universities
Universities that choose to participate interactively will develop module learning projects. This goes beyond exam engagement in real community problems.
At the same time, there will be institutional learning dashboards that accurately track every student in their engagement, participation, and concept mastery. This eventually leads to data-driven educational improvement.
Consequently, a reimagined classroom in India may assemble students into mixed-ability groups--based on the suitability of ideation capability.
For the same reason, providing them with the needed resources and tuning them to innovatively develop practicable prototypes becomes important. This ensures inclusiveness in quality education through providing every learner with a 'voice.'
Preparing Students to Fit In the Corporate & Finance Industry
Companies now require employees to adapt to AI, digitization, and changing markets.
In this scenario type, a form of deep learning through engagement means immersing the trainees in scenario-based simulations.
To be precise, it exposes students to scenes of a market crash or a change in regulations. This is better than demonstrating learning through passive lectures--dull and uninteresting without examples.
Through a data-driven education improvement approach, the organisation tracks which employees responded best to which simulations. On this basis, succession training can be conducted.
This provides the organisation with the ability to keep a future-skills-ready workforce. This happens with Artificial Intelligence in integration in eLearning--fundamentally redesigns workflows.
In the Fields of Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
Developing skills in medical education is more than just memorising anatomy or disease pathology. New models of the clinical classroom include simulation laboratories where students are learning by doing virtually.
Thus, students learn to diagnose, intervene upon, and reflect on through medical eLearning simulation--with scaffolding in place for deep learning.
Learner behaviour, decision-time, and error-types are captured and later analysed. This type of approach (data-driven educational improvement) is an asset to building subsequent modules.
This process also has positive effects for quality, inclusive education for learners with varying exposure and/or learning styles.
In pharmaceutical R&D research, interdisciplinary teams engage in live problem-solving (interactivity). In this way, it becomes possible to track results to inform training development.
Active Engagement as Pedagogical Foundation:
In contrast to the teacher-as-expert stance, the role of the educator shifts to that of a facilitator when eLearning is incorporated as a support.
Learners are called on to engage in problem-based tasks, peer engagement, and self-reflection through the eLearning medium. A learning-by-engagement stance links to deep learning outcomes.
For example, a group of renewable energy undergraduate students follows a course where each cohort builds and tests a functioning prototype solar pump. These tasks reflect on parts of the design that did not work as intended. Hence, they can be tested again with the learned theory and practice.
Using Data for Systematic Improvement and Equity
It is imperative that both school and corporate educators invest not just in the digital education tool but the analytical frameworks that use data to respond to emergent patterns.
This is where the eLearning platform comes in useful, as the recorded data contains information on captured engagement and completion progress.
The platform also allows peer-engagement or self-reflection on conceptual gaps, etc. Also, it can contextualize merit-based change in existing design for future learners.
In this fashion, organizations are also able to close equity gaps, not by being biased and reactive, but by being proactive to lower barriers for quality education for all students. The future skills classroom then becomes adaptive and personalized.
Bridging Curriculum to Future-Orientation
Let's face it: old-school teaching is just too static--may lack attention grasping elements.
Therefore, it's time for curricula to move past this onto a responsive frameworks that eLearning platforms offers.
Examples include: eLearning simulations or even complex 3D animations; both dynamic in mature with the feature of interactivity.
Importantly, what happens with it is that learners get more than just existing and known information. They are really learning how to gain new knowledge in their future.
Example: engineering students switch from textbook problems to open-ended design challenges.
This specific shift results in clear outcomes that mirror all that real-world complexity.
Let's admit it: old-school learning may sometimes get too static; the result is bored kids who fail to remember the facts.
In present times, big changes are happening and hence, it has become essential for kids must know and demonstrate the same.
At the centre: deep learning by actually participating--- courtesy eLearning platforms exhibiting numerous features.
Importantly, what happens with it is that learners really start to care as they enjoy what they learn--how wonderful is that? Importantly, students don’t just get knowledge--they start to use it in everyday life. The best exemplar would be: a health student leading a real local campaign. They recall strategies (the plans they made) longer than one reading of a book.
This way, colleges as well as schools end up building a workforce that is agile (with acquired knowledge). In simple words, what happens with it is that education tunes to adapt to the learners' needs. Meaning: the next generation of workers won’t be left behind; they will be ready for the unknown.
Benefits and Impact of This Reimagined Classroom With eLearning
More Engagement and Retention
When learners are active, they are invested; they don’t just receive knowledge--they use it. This shift to deep learning through active participation increases retention. Also, transferability of skills and curiosity among students are generated.
For example, a public-health student leading a local campaign will remember strategies longer than one who reads a textbook scenario.
Future-Proof and Responsive
Colleges and educational institutions that embed this model can help students to adapt education to future skills. They can develop w
Workforces and student bodies that are agile, resilient, and ready for change. Education for future skills means the next generation of workers won’t be obsolete--they’ll be ready for the unknown.
Equity and Inclusion via Analytics
Data-driven education opens up pathways to identify differential access or struggle for learners. eLearning provides support through instant access to everyone globally. This ensures inclusive quality education by proactively addressing exclusions. E.g., learners in remote areas or with different abilities can train whenever they want.
Synergistic Collaboration and Real-World Connectivity
With eLearning platforms, learners can do real-world tasks--simulations. This is possible in cross-disciplinary teams; students can mimic industry tasks and research environments--even before they start working.
This develops collaboration, communication, and problem-solving--skills that are transferable across sectors. Thus. business students partnering with engineering students on a sustainability pitch experience active learning.
Ultimately, an education for future skills in a redefined classroom context supports meaningful engagement. It would also lead to data-driven teaching and learning adjustments for all stakeholders.
The educated experience is one rooted in genuine engagement and intentional reflection upon the engaged experience. On the other hand, the adjustments and implications for success to come stem from data-driven recommendations offered at the next level.
This is intentional design through deep learning empowered through active participation. Best aspect: it supports the data analysis loop for collaborative, educated betterment, and always with Quality Education for All in mind. This way, an institution can equip its learning community with anything that tomorrow has to offer.
Final Reflection
Ultimately, this blog has explored how an education for future skills supports meaningful engagement. Also, data-driven educational improvement and learning adjustments for all stakeholders.
eLearning inclusion can determine how school, business and research are interconnected through actual-world experiences. It also facilitate students with multiple learning features and the deep learning necessary.
It connected the benefits--engagement, resilience, transferability, and inclusion--and challenges of assessments for accomplishments and ethics along the way.
Including eLearning can turn into a standards-based and top-down approach to teacher-centered instruction. The many-faceted features make eLearning a truly meaningful competency development. That is, from the data analysis loop to purposeful individualized learning plan accessibility. Use of eLearning platform ensures growth mindset culture, intentional engagement levels, and real-world relevance.
Institutions and colleges across India and the globe can connect with VK Creative Learning for creating a customized eLearning AI for educators benefits.
VK Creative Learning (VKCL) can provide creative hands-on engagement courses from engaged learning trends to the data-driven responsive loops. This can engage all learners at all levels of academic achievement.
Also, VK Creative Learning possesses an unmatched potential to provide truly customized content. Additionally, it offers access to engagement efforts and deliberate assessments for novice employees to seasoned ones.
For remote learning, differently-abled persons dispersed across towns and countries, VKCL supports access to learning materials.
For VKCL, Quality Education for All is not merely a goal but a proven reality. This enables workforces to be equipped for the future of work before it even comes. Thus, educators can boast of their collaborative efforts to become lifelong learners.